Unit 42, the threat intelligence team at Palo Alto Networks, has identified a sophisticated threat actor group named JavaGhost that has evolved from website defacement to executing persistent phishing campaigns using compromised AWS environments.
The group, active since at least 2022, exploits overly permissive Amazon Identity and Access Management (IAM) permissions to leverage victims’ Simple Email Service (SES) and WorkMail services for sending phishing messages.
JavaGhost’s approach is particularly effective because they utilize legitimate organizations’ AWS infrastructure, allowing their phishing emails to bypass security protections as they originate from previously trusted sources.
The group has continuously refined their tactics through 2024, implementing advanced evasion techniques to obfuscate their presence in CloudTrail logs, mirroring methods previously associated with the Scattered Spider threat group.
Initial access typically begins with the threat actors obtaining exposed long-term access keys associated with IAM users.
Unlike other attackers, JavaGhost deliberately avoids using the GetCallerIdentity API call upon entry, which helps them evade common detection methods.
Instead, they perform alternative initial API calls such as GetServiceQuota, GetSendQuota, and GetAccount to confirm their access while maintaining a lower profile.
To further hide their activities, researchers at Palo Alto Networks noted that the JavaGhost generates temporary credentials and login URLs through a multi-step process involving the GetFederationToken and GetSigninToken APIs.
This sophisticated technique allows them to access the AWS console while obfuscating their identity. An example of the inline policy used in these operations can be seen here, which shows an “allow all” policy that maximizes permissions.
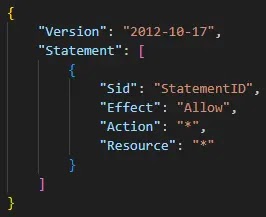
Inline policy from the GetFederationToken event (Source – Palo Alto Networks)
Phishing Infrastructure Setup
After securing console access, JavaGhost begins establishing their phishing infrastructure by creating various SES email identities and configuring DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) settings.
They modify SES Virtual Delivery Manager attributes and Mail-from settings before configuring WorkMail organizations and users.
The creation of a WorkMail organization triggers numerous SES and AWS Directory Service events in CloudTrail logs, including CreateReceiptRule, CreateReceiptRuleSet, and PutIdentityPolicy.
Prior to launching their phishing campaign, JavaGhost creates new SMTP credentials that result in the generation of IAM users with specific permissions.
Throughout their attack lifecycle, they create additional IAM users with the AWS managed AdministratorAccess policy attached, providing full permissions within the target environment.

JavaGhost website (Source – Palo Alto Networks)
The group consistently leaves their calling card by creating an EC2 security group named “Java_Ghost” with the description “We Are There But Not Visible,” matching their slogan found on their historic website.

Historic JavaGhost website (Source – Palo Alto Networks)
While their techniques continue to evolve, their activity remains detectable through careful monitoring of CloudTrail logs.




